
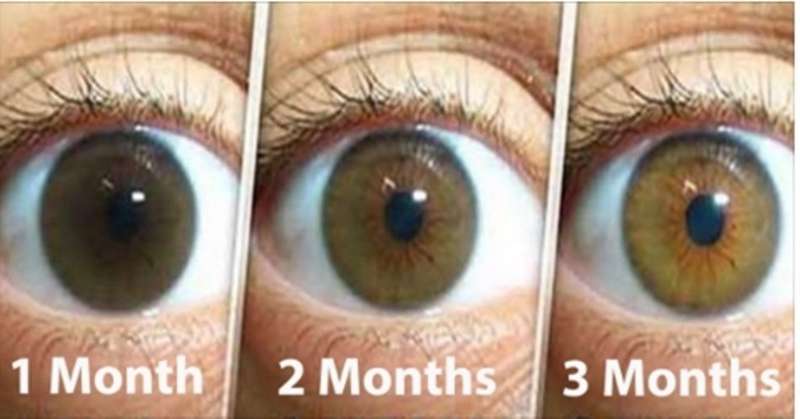















+8
Lutein 350mg 60 caps.Eye Vitamin A carotenoid.Anti cataracts,macular degen,retinitis,cancer,diabetes
Indicative market price:
R2,198.00
69% off
Shipping
R35.00 Standard shipping using one of our trusted couriers applies to most areas in South Africa. Some areas may attract a R30.00 surcharge. This will be calculated at checkout if applicable.
Check my rate
Check my rate
The seller has indicated that they will usually have this item
ready to ship within 1 business day.
Shipping time depends on your delivery address.
The most accurate delivery time will be calculated at checkout,
but in general, the following shipping times apply:
Standard Delivery
| Main centres: | 1-3 business days |
| Regional areas: | 3-4 business days |
| Remote areas: | 3-5 business days |
Seller
Age Smart Nutrition(Blacklisted)
Buyer protection
Returns
Get it now, pay later
















.jpg)
.png)
